CS224W Lecture 4 Link Analysis: PageRank
introduction
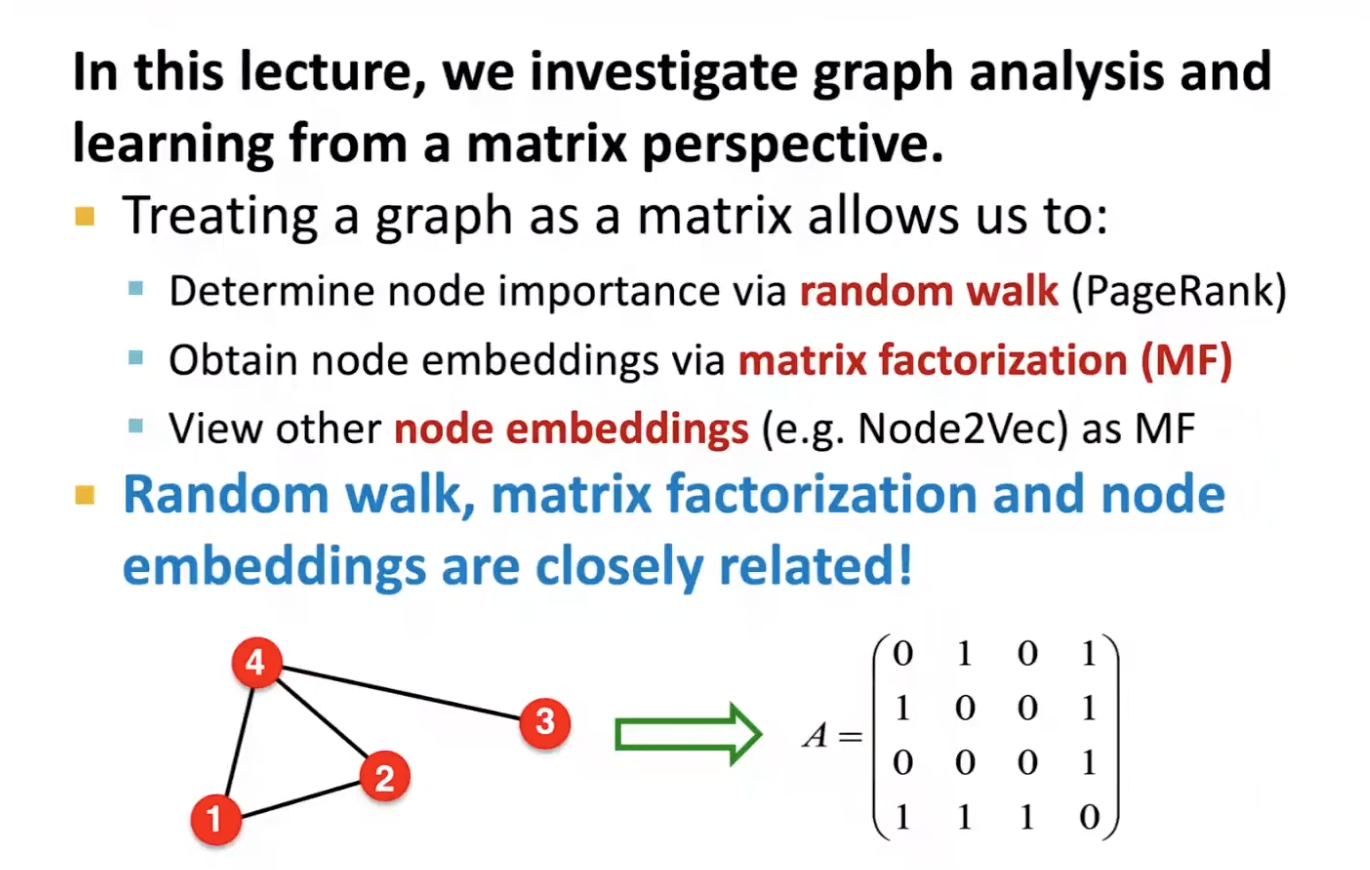
- the web as a graph
- nodes: webpage, edges: hyperlinks
- directed graph
- all nodes are not equally important
- => rank the pages using link structure
- link analysis algorithm (to compute importance of nodes)
- page rank
- personalized page rank (PRR)
- random walk with restarts
PageRank
- Links as votes

- => page rank
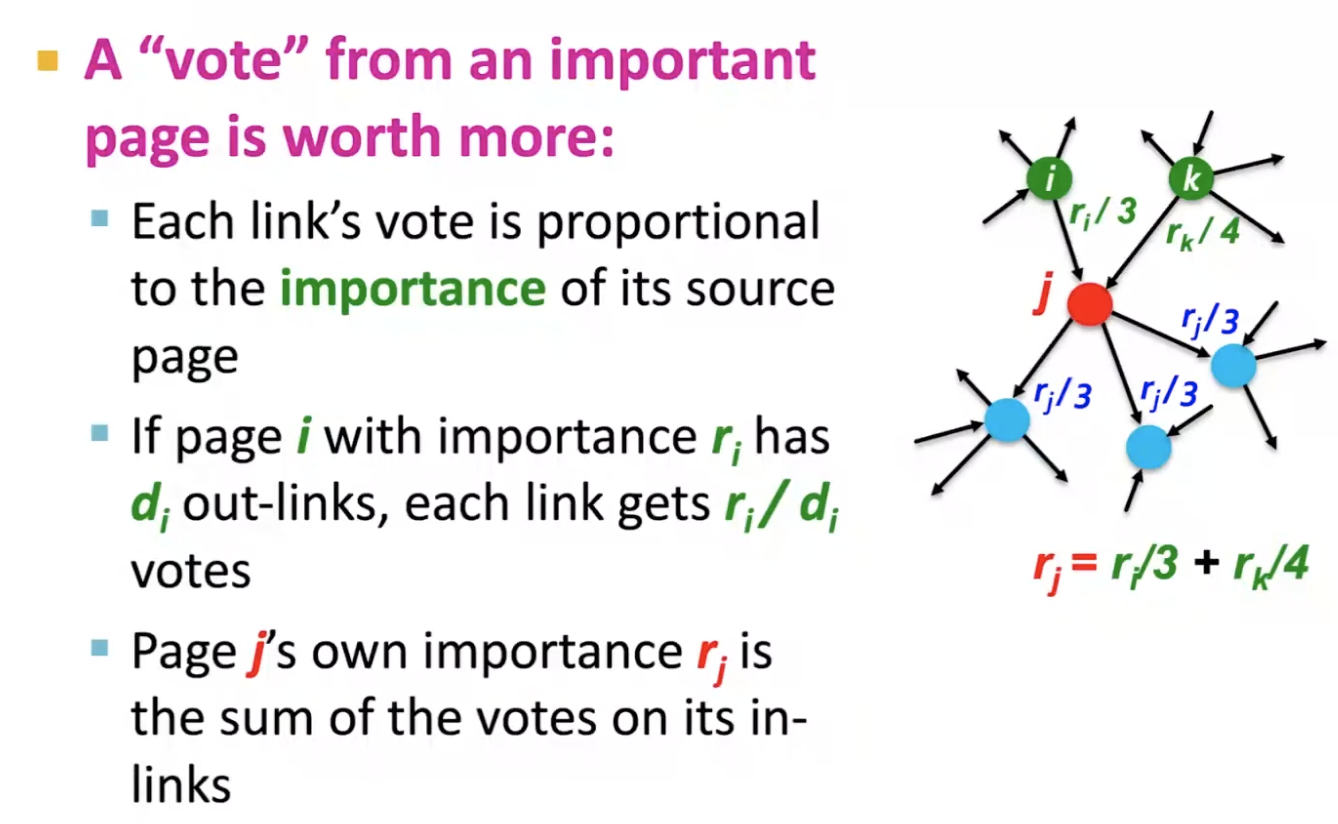
- long term distribution of the surfers
- page rank: pincipal eigenvector of stochastic adjacency matrix
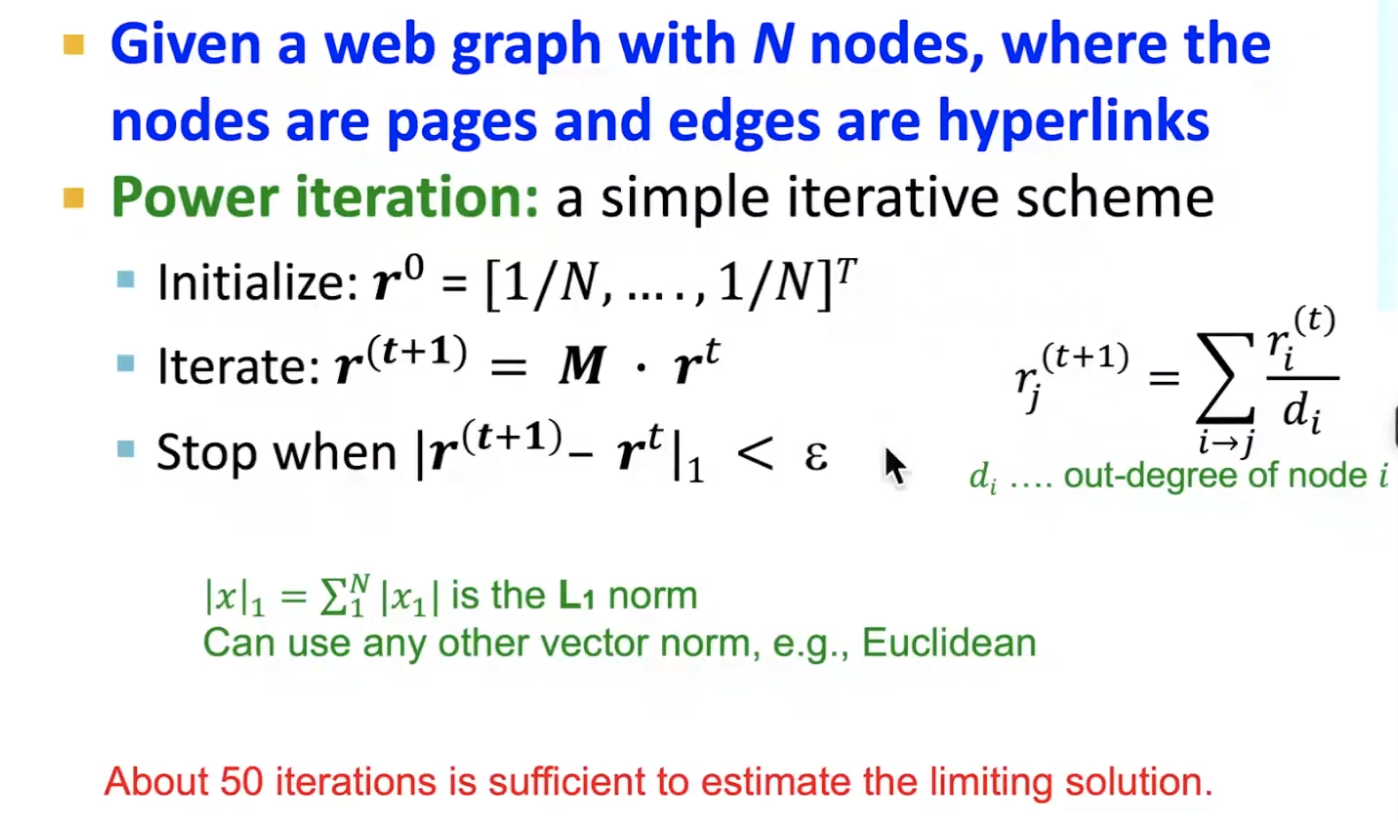
- we can efficiently solve with power iteration.
- page rank summary

-
how to solve pagerank
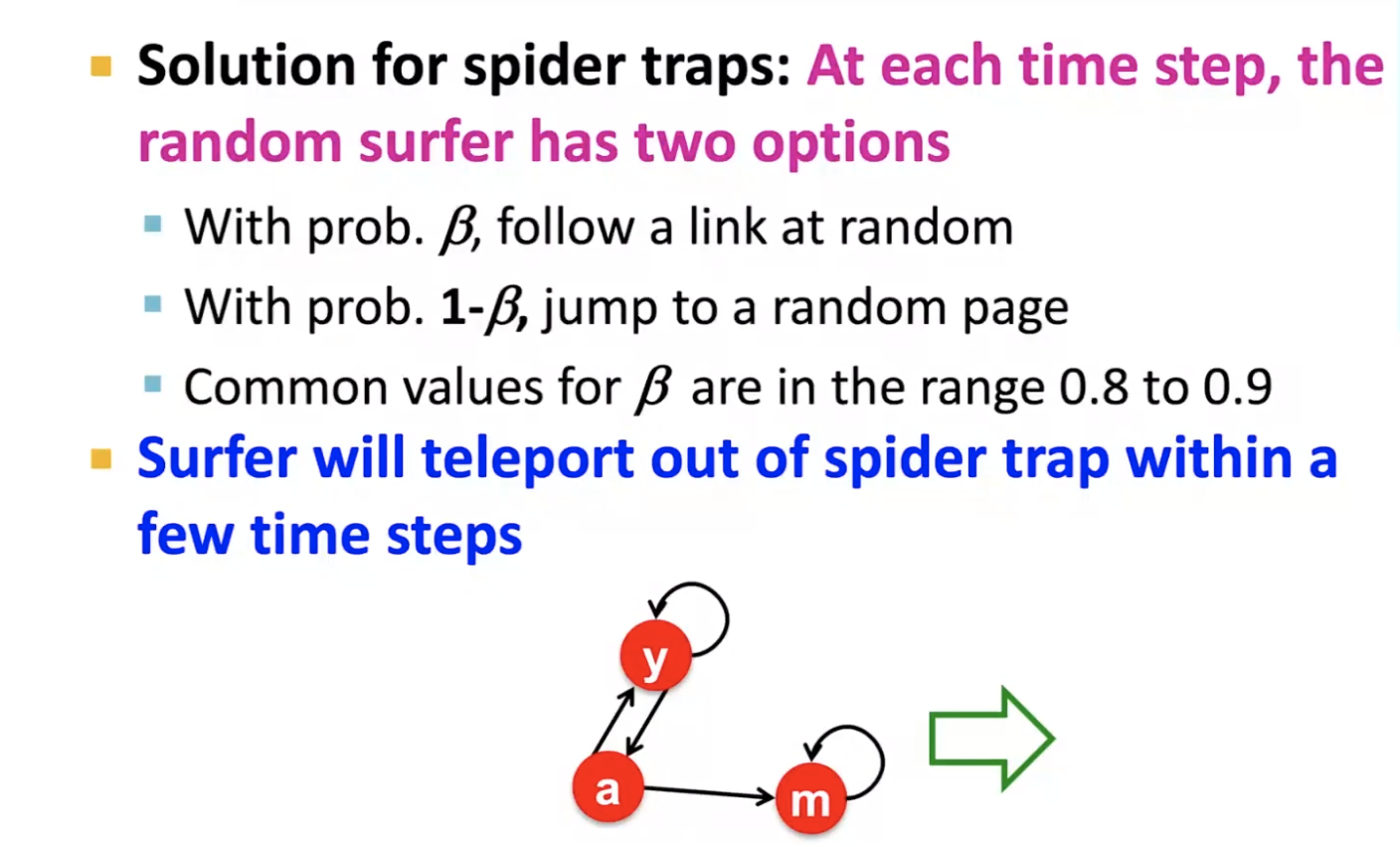
- problem:
- spider trap (all out links are within the group)
- spider traps are not a problem, but with traps, page rank scores are not what we want
- solution: random jump (or teleport)
- some pages are dead ends (no out link)
- dead ends are a problem
- solution: 100% teleport
- spider trap (all out links are within the group)
- problem:

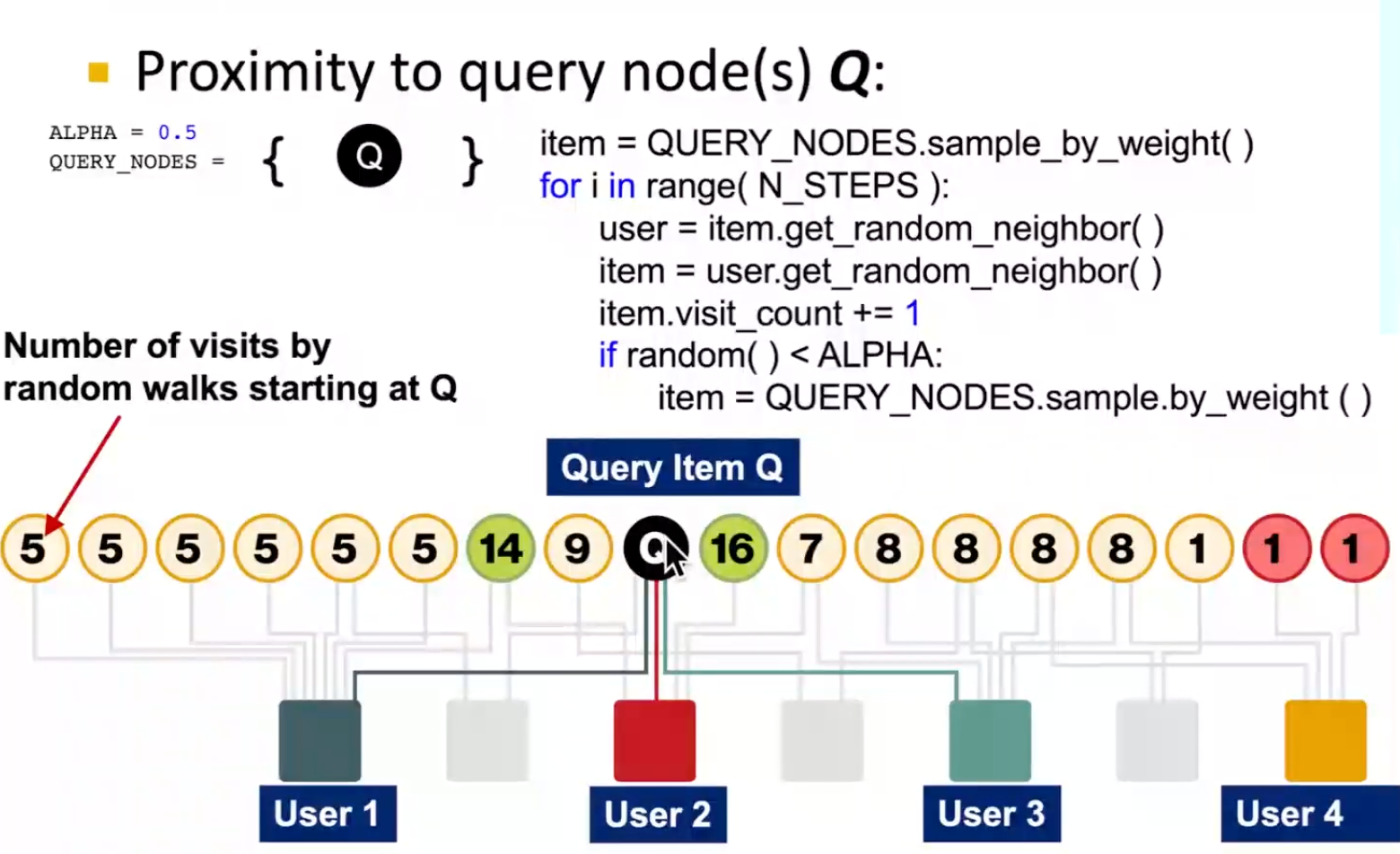
Random Walk with Restarts and Personalized PageRank


Matrix Factorization and Node Embeddings
- simplest approach -> embedding lookup
- =>

- limitation:
- cannot obtain embeddings for nodes not in the trainset
- cannot capture structural similarity
- cannot utilize node, edge, and graph features
November 11, 2021
Tags:
cs224w